Toyota cars are known for their quality and reliability. However, like any other car, they can have problems from time to time. One of the most common problems is the P0420 code. In this post, we will discuss the meaning of the P0420 code in a Toyota, its causes, symptoms, and fixes.
The P0420 code is a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) for “Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold”, meaning that the vehicle’s emissions output may be higher than normal.
Toyota P0420 Code Causes
1. Faulty Oxygen Sensor
The oxygen sensor is responsible for monitoring the air/fuel mixture. It works by measuring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. If there is too much oxygen, it means that the mixture is too lean. Conversely, if there is not enough oxygen, it means that the mixture is too rich.
2. Faulty Air-Fuel Sensor
The air-fuel sensor is responsible for monitoring the air-to-fuel ratio. It works by measuring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas. If there is too much oxygen, it means that the air-fuel mixture is too lean.
3. Leak in the Exhaust System

A leak in the exhaust system can cause the P0420 code to trigger. The most common cause of this is a cracked exhaust manifold. When the exhaust manifold cracks, the gas will leak out and cause the P0420 code to trigger.
4. Engine Misfire
When you’re getting a P0420 code on your Toyota, you’re likely experiencing a misfire or a rough idle. These are both common symptoms of this particular code, and they can be caused by several different things.
In most cases, it’s due to an issue with the catalytic converter, but it could also be due to a problem with the oxygen sensor, the spark plugs, or the fuel injectors.
In case you’re experiencing a misfire, likely, one or more of your cylinders is not functioning correctly. This can cause a rough idle and may even cause your engine to stall. In some cases, you may also notice a decrease in power and fuel economy.
5. Leaded Gasoline
While leaded gasoline is not as common as it used to be, it can still be a cause of the P0420 code in Toyota vehicles. If your vehicle was built before 1996, you are likely using leaded gasoline.
If you have recently switched to unleaded gasoline and are still getting the P0420 code, this could be the cause. Lead deposits can build up on the oxygen sensor and prevent it from working properly.
6. Rich or Lean Fuel Ratio
A P0420 code may be caused by a rich or lean fuel condition. If the air/fuel mixture is too rich, it will cause the oxygen sensor to produce a false lean signal. Conversely, if the mixture is too lean, it will cause the oxygen sensor to produce a false rich signal.
When your Toyota’s OBD-II system detects a lean condition (too much air and not enough fuel), it will set a P0420 code. A rich condition (too much fuel and not enough air) will cause the OBD-II system to set a P0421 code.
When troubleshooting this code, it is important to check the fuel trim values. If the fuel trim values are within normal range, then the problem is most likely caused by an exhaust leak.
7. Damaged Catalytic Converter
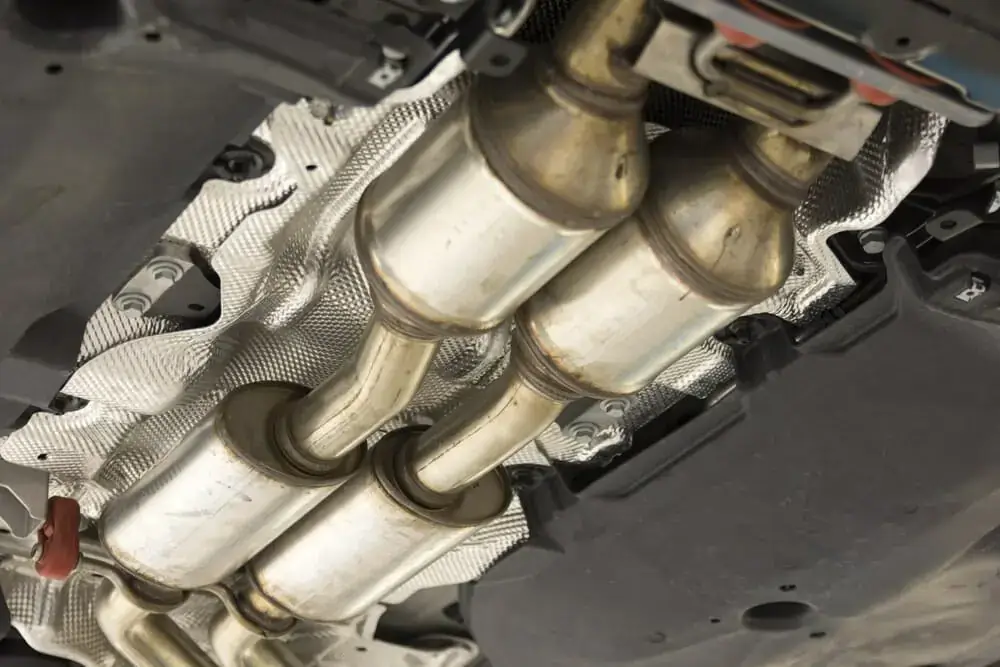
This is the most common cause of the P0420 code. The catalytic converter is a vital part of your car’s emissions control system, and it helps to convert harmful gases into less harmful ones. A damaged catalytic converter can’t do its job properly, and this will trigger the P0420 code.
8. Wrong Placement of Catalytic Converter
Another reason your check engine light may be triggered is due to the catalytic converter being placed in the wrong spot. When the catalytic converter is placed too close to the engine, it can overheat and cause damage. This will trigger the P0420 code.
9. Oil Contamination in the Catalytic Converter
When your engine oil breaks down, it can contaminate the catalytic converter. This will cause the catalytic converter to fail and the P0420 code to be triggered. You’ll need to change your oil and filter to fix this problem.
Toyota P0420 Code Symptoms
The most common symptom of the P0420 code are:
1. Check Engine Lights On
This is the most common symptom of the P0420 code. The catalytic converter is an emission control device, so when it’s not functioning properly, the Check Engine Light will come on until the problem is fixed.
2. Decreased Fuel Economy

When the catalytic converter isn’t operating properly, your car will have to work harder to make the same amount of power. This puts extra strain on the engine, which can lead to decreased fuel economy.
If you notice that your gas mileage has decreased significantly, it could be due to a problem with the catalytic converter.
3. Lack of Power From the Engine
A catalytic converter that is not working properly will cause the engine to run less efficiently. This can lead to a loss of power, which may be one of the first symptoms you notice. If your Toyota has this problem, it may also produce black smoke from the exhaust pipe.
4. Sulfur Smell
When your Toyota is burning sulfur, it will produce a rotten egg smell. If you notice this while your car is running, take it to a mechanic right away as it indicates that your catalytic converter needs to be replaced.
How to Fix P0240 Toyota Code
There are a few things you can do to try and fix this code yourself including:
- Cleaning The Catalytic Converter
- Replace Catalytic Converter
- Replace Front or Rear Oxygen Sensor
- Repair Damaged Sensor Wiring
- Fix Oil Burn
- Fix Misfires
- Fix Lean or Rich Fuel Mixture
- Replace Engine Control Unit
Conclusion
A P0420 code in a Toyota means there’s a problem with the catalytic converter. The most common cause is a faulty oxygen sensor, but it could also be caused by a loose gas cap or a problem with the engine.


